Introduction:
The manufacturing industry is on the brink of a profound transformation, driven by rapid advancements in automation technologies. From robotics and artificial intelligence to the Internet of Things (IoT) and digital twins, automation is revolutionizing how goods are produced, increasing efficiency, agility, and competitiveness. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key trends and predictions shaping the future of automation in manufacturing and how businesses can navigate this evolving landscape to stay ahead of the curve.
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with factory automation has emerged as a game-changer, reshaping traditional production processes and paving the way for unprecedented efficiency and innovation.
Robotics and Cobots:
Robots have long been a staple of manufacturing automation, but the rise of collaborative robots, or cobots, is taking automation to new heights. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots are designed to work alongside humans, augmenting their capabilities and enhancing productivity. As cobots become more affordable, adaptable, and user-friendly, we can expect to see widespread adoption across manufacturing facilities, particularly in industries with high labor costs or repetitive tasks.

The Evolution of Robotics in Manufacturing: Robotics have long been a staple in manufacturing, automating repetitive tasks and enhancing productivity. Traditional industrial robots have excelled in tasks requiring speed, precision, and consistency,
Introducing Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Collaborative robots, or cobots, represent a paradigm shift in robotics by enabling safe and seamless interaction between humans and machines.
Enhancing Safety and Ergonomics:
Cobots prioritize safety and ergonomics, minimizing the risk of workplace injuries and ergonomic strain. With built-in sensors and collision detection algorithms, cobots can detect the presence of humans in their vicinity and adjust their speed and trajectory accordingly.
Flexibility and Adaptability: One of the key advantages of cobots is their flexibility and adaptability to changing production needs. Unlike traditional robots, which are often fixed in place and dedicated to specific tasks, cobots can be easily reprogrammed and redeployed for different applications.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are driving significant advancements in manufacturing automation, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. As AI technologies continue to mature, we can anticipate their integration into various aspects of manufacturing operations, from supply chain management to production planning.

Predictive Maintenance: AI and ML algorithms are revolutionizing maintenance practices by enabling predictive maintenance strategies. By analyzing equipment data in real-time, these algorithms can identify patterns indicative of potential failures,
Quality Control and Defect Detection: AI-powered quality control systems leverage computer vision and machine learning techniques to inspect products for defects with unparalleled accuracy and speed.
Optimized Production Planning: AI and ML algorithms are revolutionizing production planning by enabling dynamic, data-driven decision-making. These algorithms analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time data to optimize production schedules,
Supply Chain Management: AI and ML technologies are transforming supply chain management by enabling real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and automation. These technologies analyze diverse data sources, such as customer,
Future Outlook: As AI and ML technologies continue to advance, their impact on manufacturing will only grow. Future developments may include autonomous manufacturing systems.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Factories:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing manufacturing through connected devices, sensors, and data analytics, enabling the creation of smart factories. IoT-enabled equipment and machinery can communicate and collaborate.
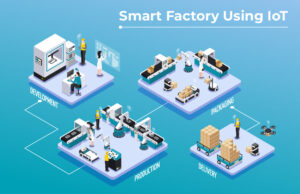
autonomously, optimizing production processes, monitoring performance, and detecting issues before they escalate. With the proliferation of IoT devices and advancements in connectivity and data analytics, smart factories will become increasingly prevalent, driving efficiency, agility, and cost savings.
Digital Twins and Simulation:
Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, are reshaping manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization. By creating digital twins of production lines, equipment, and entire factories, manufacturers can simulate scenarios, identify bottlenecks, and optimize performance without disrupting operations. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, digital twins will play a central role in driving innovation and continuous improvement in manufacturing.
Human-Machine Collaboration and Reskilling:
As automation proliferates in manufacturing, there’s a growing emphasis on human-machine collaboration and workforce reskilling. Rather than replacing human workers, automation technologies are augmenting their capabilities and enabling them to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. Manufacturers must invest in workforce development initiatives, training programs, and upskilling efforts to ensure that employees are equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in an increasingly automated environment.

The Evolution of Human-Machine Collaboration: Human-machine collaboration represents a departure from traditional manufacturing models, where humans and machines operated in separate spheres.
Empowering Workers through Reskilling: As automation reshapes job roles and tasks in manufacturing, there is a growing need to reskill and upskill the workforce to remain competitive in the industry.
Fostering a Culture of Lifelong Learning: In the face of rapid technological advancement, reskilling is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Manufacturers must foster a culture of lifelong learning and continuous improvement to ensure that their workforce remains adaptable and resilient in the face of change.
Building Cross-Disciplinary Skills: Human-machine collaboration requires workers to possess a diverse set of skills that span technical, analytical, and interpersonal domains. In addition to technical competencies, such as programming and data analysis,
The Future of Work in Manufacturing: In the future, human-machine collaboration will continue to evolve, with advancements in robotics, AI, and automation reshaping the nature of work in manufacturing.
Conclusion:
The future of automation in manufacturing is bright and full of promise, driven by technological advancements, innovation, and a relentless pursuit of efficiency and excellence. By embracing emerging trends such as robotics, artificial intelligence, IoT, digital twins, and human-machine collaboration, manufacturers can unlock new levels of productivity, agility, and competitiveness. As we navigate this transformative journey, it’s essential for businesses to stay informed, adaptable, and forward-thinking, leveraging automation technologies to drive continuous improvement and success in the dynamic world of manufacturing.

