Introduction:
In the realm of technological evolution, nanotechnology stands out as a pioneering field, offering boundless possibilities on a minuscule scale. From healthcare to electronics, its impact is reshaping industries, ushering in an era of unparalleled innovation. In this blog, we embark on a journey through the world of nanotechnology gadgets, exploring the transformative power of these miniature marvels.
In the vast landscape of technological innovation, few fields hold as much promise and intrigue as nanotechnology. At its core, nanotechnology involves the manipulation of matter at the nanoscale – a scale so small that it operates at the level of individual atoms and molecules. This ability to engineer materials and devices at such a minute scale opens up a world of possibilities, giving rise to a new generation of gadgets that are revolutionizing various industries.
What is Nanotechnology?
Nanotechnology is a multidisciplinary field of science and engineering that deals with the manipulation of matter at the nanoscale, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers (one billionth of a meter). At this scale, materials and devices exhibit unique properties and behaviors that differ from those at larger scales.
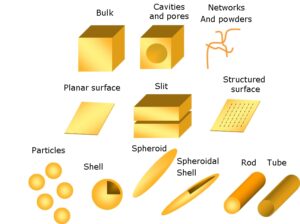
Miniaturization: Nanotechnology enables the creation of structures and devices with dimensions on the nanoscale, leading to miniaturization and increased surface area-to-volume ratios.
Unique Properties: Materials at the nanoscale often exhibit unique properties, such as quantum effects, increased strength, enhanced conductivity, and improved catalytic activity.
Interdisciplinary Approach: Nanotechnology draws upon knowledge and techniques from diverse fields, including physics, chemistry, biology, and engineering.
Applications: Nanotechnology has numerous applications across various sectors, including electronics, healthcare, energy, environmental remediation, and materials science. manufacturing.
Challenges and Considerations: Despite its promising potential, nanotechnology also presents challenges and considerations, such as safety concerns regarding the potential toxicity of nanomaterials,
Nanotechnology in Consumer Gadgets:
Nanotechnology has made significant strides in revolutionizing consumer gadgets across various categories, offering enhanced performance, durability, and functionality. Here’s how nanotechnology is transforming consumer gadgets.

Smaller and Lighter Devices: Nanotechnology enables the miniaturization of electronic components, allowing manufacturers to create smaller and lighter gadgets without compromising performance.
- Improved Display Technology:
Nanotech-enabled materials, such as quantum dots and nanocrystals, are used in display panels to enhance brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency.
Quantum dot displays offer vibrant colors and high-resolution images, leading to superior viewing experiences in gadgets like smartphones, TVs, and monitors.
- Enhanced Battery Performance:
Nanomaterials, such as nanostructured electrodes and electrolytes, improve the energy storage and efficiency of batteries used in consumer gadgets.
Nanotech advancements extend battery life, reduce charging times, and enhance overall power performance, addressing one of the most critical concerns for gadget users.
- Scratch-Resistant Surfaces:
Nanotechnology helps protect device screens, casings, and other vulnerable components from scratches, abrasions, and wear, prolonging their lifespan and maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Nanotech Materials:
Nanotechnology has introduced a diverse range of nanomaterials that are revolutionizing consumer gadgets. These materials exhibit unique properties and functionalities at the nanoscale, contributing to the development of smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices. Here are some notable nanotech materials used in consumer gadgets:
- 1. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs):
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical structures composed of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice.
CNTs exhibit exceptional mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity, making them valuable in various gadget applications.
- Nanocomposites:
Nanocomposites are materials composed of a combination of nanoparticles and a matrix material, such as polymers or metals.
They exhibit enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties compared to conventional materials.
- Graphene:
Graphene is used in gadgets for applications such as flexible displays, transparent electrodes, and high-performance batteries, enabling innovative device designs and functionalities.
- Nanowires:
Nanowires are ultra-thin wires with diameters on the nanoscale, typically composed of materials like silicon, gold, or silver.
Benefits of Nanotechnology Gadgets:
Nanotechnology has brought about numerous benefits to consumer gadgets, enhancing their performance, durability, and functionality. Here are some of the key advantages of nanotechnology in gadgets:

- Improved Performance:
Enhanced Efficiency: Nanomaterials enable the design of more efficient electronic components, such as transistors and batteries, leading to improved energy efficiency and longer battery life in gadgets.
Faster Processing: Nanoscale structures facilitate faster data processing and transmission speeds in devices like smartphones and computers, resulting in smoother performance and reduced lag.
Miniaturization: Smaller Form Factor: Nanotechnology enables the miniaturization of electronic components, allowing manufacturers to create smaller and lighter gadgets without sacrificing performance.
Increased Portability: Compact devices made possible by nanotech innovations, such as smartphones and wearables, offer increased portability and convenience for users.
Enhanced Display Technology: Vibrant Colors: Quantum dot displays, enabled by nanotechnology, deliver vibrant colors and high-resolution images, enhancing the visual experience for users of smartphones, TVs, and monitors.
Smart Materials: Nanotech-enabled smart materials respond to external stimuli, enabling innovative functionalities like self-healing surfaces, shape memory alloys, and adaptive coatings in gadgets
Challenges and Limitations:
Certainly! Despite its promise, nanotechnology also presents several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed:

- Safety Concerns:
Toxicity: Some nanomaterials may pose health risks if they are released into the environment or come into contact with living organisms. Understanding and mitigating the potential toxicity of nanomaterials is crucial for their safe use in consumer gadgets.
- Scalability and Manufacturing: Cost of Production: Nanotechnology often involves complex manufacturing processes and specialized equipment, leading to higher production costs for nanotech-enabled gadgets. Scaling up production while keeping costs manageable remains a challenge.
- Performance Stability:
Reliability: The performance of nanotech-enabled gadgets may be affected by factors such as environmental conditions, material degradation, and manufacturing variations.
Future Outlook:
The future of nanotechnology in consumer gadgets holds tremendous promise for transforming the way we interact with technology, enhancing our daily lives, and addressing global challenges in sustainability, connectivity, and health. As research and innovation in nanotechnology continue to accelerate, we can expect to see increasingly innovative and disruptive advancements in consumer electronics in the years to come;
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the exploration of nanotechnology gadgets reveals a world of miniature marvels that are transforming technology as we know it. With innovations in materials science, device design, energy storage, sensing capabilities, and sustainability, nanotechnology is driving unprecedented advancements in consumer gadgets. From flexible displays to smart wearables and eco-friendly solutions, nanotech-enabled gadgets are reshaping the future of tech, promising enhanced performance, durability, and functionality for users worldwide.

