Introduction:
Blockchain Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has evolved into a versatile and impactful technology with applications beyond digital currencies. Here are several areas where blockchain technology is making a significant impact:
Blockchain technology, originally popularized by cryptocurrencies likeBitcoin, has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with far reaching implications beyond currencies.
The entire lands of financial service. Let’s explore some of the key blockchain applications in finance and banking. This design ensures transparency, security, and immutability that have fueled its adoption in various.

This can automate and streamline various processes in industries such as legal, real estate, and supply chain. As blockchain technology continues to mature, its applications are likely to expand further across various,
Blockchain technology has diverse applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chain management, healthcare, finance, voting systems, and more. Its key advantages include transparency, security, immutability, Blockchain technology has applications beyond cryptocurrencies,
What is Blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that enables secure and transparent record-keeping of digital transactions across a network of computers, It is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies.
Decentralization: known as a node, has a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring that no single entity has complete control. and there is no central authority controlling the system.
Blocks: Transactions are grouped together into blocks, and each block contains a reference to the previous block, forming a chain. This chaining of blocks is what gives the technology its name.
Cryptographic Hash Functions: Each block contains a unique identifier called a cryptographic hash, which is generated based on the information within the block. Any alteration to the block would require changes to subsequent blocks, making the blockchain resistant to tampering.
Public vs. private Blockchains: Public blockchains are open to anyone, while private blockchains restrict access to a specific group of participants. Public blockchains are typically associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and while private blockchains are often used in enterprise settings.
Challenges faced in Adopting Blockchain technology?
While blockchain technology offers various benefits, its adoption comes with several challenges. Here are some common challenges faced in adopting blockchain technology:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Many countries lack clear regulations around blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Uncertainty in legal frameworks can hinder adoption as businesses may fear legal consequences or compliance issues.

Interoperability: Different blockchain platforms may use distinct protocols and standards, leading to interoperability challenges. Integrating blockchain with existing systems can be complex and may require significant effort.
Scalavbility: Scalability is a critical issue, especially for public blockchains. As the number of users and transactions increases, the network may struggle to handle the load efficiently, resulting in slower transaction speeds and higher fees.
Lack of Standardization: The absence of widely accepted standards poses a challenge for developers and organizations. Standardization is crucial for interoperability, seamless integration, and the development of a robust blockchain ecosystem.
The Future of Blockchain Technology?
As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, I don’t have real-time information on developments in blockchain technology. However, I can provide some general trends and possibilities that were anticipated for the future of blockchain technology based on information available up to that point.
Scalability Improvements: Blockchain systems have faced challenges with scalability, limiting their transaction throughput. such as sidechains and state channels) and improvements to the underlying consensus algorithms.
Smart Contract Evolution: Smart contracts were expected to evol

ve with more sophisticated functionalities, improved security, and easier development tools. This could lead to increased adoption of decentralized applications across various industries.
Integration with Traditional Systems: The integration of blockchain technology with traditional systems and businesses was predicted to increase. Hybrid models, where blockchain is used alongside existing technologies.
Focus on privacy security: Enhanced privacy features and security measures were anticipated to be integrated into blockchain systems. Privacy-focused cryptocurrencies and zero-knowledge proof technologies were gaining attention.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrencies?
Blockchain technology has proven to have applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Here are several use cases across various industries:
Its decentralized and tamper resistant nature makes it applicable to a wide array of use cases.
Blockchain, originally designed as the under technology for cryptcurrencies like bitcoin, has evolved far beyond its initial purpose.
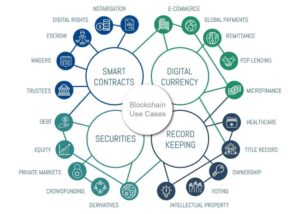
Supply chain Management:
: Provence Tracking: Blockchain can be used to trace the origin and journey of products in the supply chain, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of fraud.
Real time Monitoring: Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate and enforce agreements between parties in the supply chain, ensuring compliance and efficiency.
Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store and manage patient records, ensuring data integrity and facilitating secure sharing of medical information among authorized parties. It can be used to track the entire pharmaceutical supply chain, reducing the chances of counterfeit drugs entering the market.
Intellectual Property protection: Blockchain can be used to track and manage digital content rights, protecting intellectual property and ensuring fair compensation for creators. Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent platform for registering and managing patents and trademarks.
Education:
Credential verification: Blockchain can be used to verify and store educational credentials, reducing the risk of fake diplomas and enhancing the credibility of qualifications.
Voting System:
Secure Voting: Blockchain can enhance the security and transparency of voting systems by providing an immutable record of votes, reducing the risk of tampering or manipulation.
Remote Voting: Blockchain can enable secure and verifiable remote voting systems.
Finance and Banking:
Cross border Payments: Blockchain facilitates faster and cheaper cross-border transactions by eliminating intermediaries and providing a decentralized ledger for transactions.
Smart Contracts for Financial Agreements: Automating and enforcing financial contracts through smart contracts can reduce errors and fraud.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Blockchain technology transcends its origins in cryptocurrencies, evolving into a transformative force across diverse industries. Beyond its role in secure and transparent financial transactions, Blockchain fosters decentralized systems, enhancing data integrity, and reducing fraud. Industries such as healthcare, supply chain, and logistics benefit from its immutable ledger, ensuring trust and accountability. Smart contracts, enabled by Blockchain, automate agreements, streamlining processes and reducing costs. As a catalyst for innovation, Blockchain paves the way for a more efficient and inclusive digital future. Its potential to revolutionize traditional structures underscores its significance, heralding a new era of decentralized, transparent, and secure systems beyond the realm of cryptocurrencies.

