Introduction:
Introduce the concept of biometric payment systems and their increasing prevalence in the modern world. Highlight the significance of using unique biological identifiers for secure transactions.
Absolutely! Biometric payment systems represent an innovative approach to secure transactions by leveraging unique biological identifiers such as fingerprints and facial features.
Define biometric payment systems and their significance in modern transaction security.
Introduce the use of fingerprint and face recognition as authentication methods.
Highlight the importance of securing transactions in an increasingly digital world.
- Understanding Biometric Payment Systems:
Define biometric payment systems and their significance in modern transactions.
Highlight the increasing adoption of biometric authentication methods in various industries.
What are Biometric Payment Systems:
Explain the concept of biometric authentication in payment systems.
Define biometrics and its role in verifying the identity of users.
How do Biometric Payment Systems Work:
Describe the process of biometric authentication in payment transactions.
Explain the steps involved in capturing and verifying biometric data.
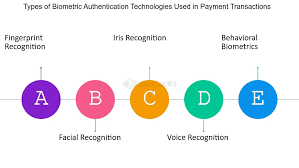
Types of Biometric Authentication Methods:
Explore various biometric modalities used in payment systems, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, voice recognition, etc.
Compare the strengths and weaknesses of different biometric authentication methods.
Advantages of Biometric Payment Systems:
Examine the benefits of using biometric authentication for payment transactions.
Discuss the convenience, speed, and accuracy of biometric payments.
- Fingerprint Recognition Technology:
Detail the technology behind fingerprint recognition.
Explain the process of capturing and analyzing fingerprint data for authentication.
Discuss the reliability and security of fingerprint-based biometric payment systems.
Briefly introduce the concept of fingerprint recognition technology.
Highlight its widespread use in various applications, from security systems to mobile devices.
How Fingerprint Recognition Works:
Explain the biological uniqueness of fingerprints.
Describe the process of capturing fingerprints using sensors.
Detail the steps involved in fingerprint recognition, including image processing and feature extraction.
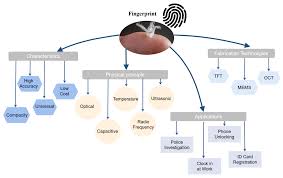
Types of Fingerprint Patterns:
Introduce the different types of fingerprint patterns, such as loops, whorls, and arches.
Explain how these patterns are used in fingerprint recognition algorithm
Fingerprint Recognition Algorithms:
Explore various algorithms used in fingerprint recognition, such as minutiae-based matching and ridge-based matching.
Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of each algorithm.
Fingerprint Sensors:
Describe the types of fingerprint sensors commonly used in devices, including optical, capacitive, and ultrasonic sensors.
Explain how each type of sensor works and its advantages in different applications.
Applications of Fingerprint Recognition:
Provide examples of real-world applications of fingerprint recognition technology, such as access control systems, mobile devices, and forensic analysis.
Discuss the advantages of using fingerprints for authentication in various contexts.
- Face Recognition Technology:
Explore the use of facial recognition in biometric payment systems.
Describe how facial features are captured and utilized for authentication purposes.
It works by analyzing patterns, shapes, and features of a person’s face and comparing them to a database of known faces.

Face Detection:
The first step in face recognition involves detecting and locating faces within an image or video frame. This process identifies the presence and location of faces, typically by detecting facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth.
Feature Extraction:
Once faces are detected, the system extracts distinctive features from the faces, such as the distance between eyes, the shape of the nose, and the contours of the face.
Face Matching:
The extracted features are compared against a database of stored face templates. This comparison process involves measuring the similarity between the features of the detected face and those in the database.
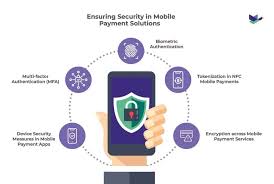
- Security and Privacy Considerations:
Address security concerns related to biometric payment systems, such as potential spoofing or hacking attempts. Discuss the measures taken to safeguard biometric data and ensure user privacy. Highlight regulatory frameworks like GDPR and CCPA governing biometric data usage.
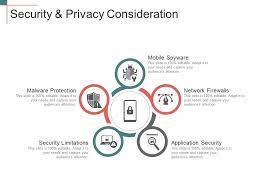
Security and privacy considerations are paramount when deploying face recognition technology due to its potential impact on individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Data Security:
Face recognition systems typically rely on large databases of face images or templates. It’s crucial to secure these databases against unauthorized access, hacking, or data breaches.
Biometric Data Protection:
Facial biometric data is highly sensitive and unique to individuals. Organizations must implement robust measures to protect this data, including encryption, anonymization techniques.
Security Against Spoofing:
Face recognition systems can be vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where adversaries use fake or manipulated facial images to bypass authentication.
- Advantages of Biometric Payment Systems:
Outline the benefits of using biometric authentication for payments. Discuss the convenience and efficiency of biometric transactions, as well as the reduced risk of identity theft and fraud. Provide real-world examples of successful biometric payment implementations.
Biometric payment systems offer several advantages over traditional payment methods, providing convenience, security, and efficiency.
Enhanced Security:
Biometric authentication adds an extra layer of security compared to traditional methods such as PINs or passwords. Biometric features like fingerprints, facial recognition.
Reduced Fraud:
Biometric authentication significantly reduces the risk of fraud and identity theft. Since biometric traits are difficult to replicate or forge,it becomes challenging for fraudsters to gain unauthorized access to accounts or make fraudulent transactions.
Convenience: Biometric payment systems offer a convenient and seamless user experience. Users no longer need to remember passwords or carry physical cards, reducing the likelihood of forgetting or losing them.
Improved User Experience:
Biometric payment systems enhance the overall user experience by simplifying the authentication process.
Future-Proof Technology:
Biometric payment systems represent a forward-thinking approach to payment technology. As biometric authentication becomes more widespread and accepted.
- Challenges and Limitations:
Acknowledge the challenges and limitations of biometric payment systems, including technological constraints and user acceptance issues. Discuss potential improvements and future developments in biometric authentication technology.
While biometric payment systems offer numerous advantages, they also face several challenges and limitations:
Privacy Concerns:
One of the primary challenges with biometric payment systems is privacy. Collecting and storing biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial features, raises concerns about data security and potential misuse.
Data Security Risks:
Biometric data is highly sensitive and irreplaceable, making it a lucrative target for hackers and cybercriminals. If biometric databases are compromised.
Accuracy and Reliability:
Biometric authentication systems are not infallible and may encounter errors or false positives/negatives.
Spoofing and Biometric Forgery:
Biometric systems are susceptible to spoofing attacks, where adversaries attempt to deceive the system by presenting fake or manipulated biometric traits.
- Adoption and Future Trends:
Examine the current adoption rates of biometric payment systems across different industries and regions. Discuss emerging trends such as the integration of biometrics into wearable devices and smart appliances.
Adoption of biometric payment systems has been steadily increasing, driven by advancements in technology, growing concerns about security, and the demand for convenient payment solutions.
Consumer Demand for Convenience and Security:
Consumers increasingly seek convenient and secure payment methods that streamline the checkout process.
Rise of Contactless Payments: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of contactless payment methods, including biometric payments.
Integration with Mobile Devices:
Biometric authentication features, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition, are becoming standard features in smartphones and tablets.
Advancements in Biometric Technology:
Ongoing advancements in biometric technology, including improved algorithms, sensors, and hardware, are enhancing the accuracy, reliability, and usability of biometric payment systems.
Biometric Wearables and IoT Devices:
The integration of biometric authentication into wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, opens up new opportunities for biometric payment systems.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, biometric payment systems leveraging fingerprint and face recognition offer a robust solution for securing transactions. With their unique biometric identifiers, users can enjoy enhanced security and convenience. As technology advances and privacy concerns are addressed, biometric authentication is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of secure digital transactions.

